Introduction: E-Business
Introduction: E-Business
E-business refers to all uses of advances in information technology (IT), particularly networking and communications technology, to improve the ways in which an organisation performs all of its business processes.
E-business encompasses an organization’s external interactions with its:
- Suppliers
- Customers
- Investors
- Creditors
- The government
- Media
E-Business Models
- Business to Consumers (B2C): Interactions between individuals and organizations.
- Business to Business (B2B): Interorganizational e-business.
Categories of E-Business
E-Business Effects on Business Processes
- Electronic Data Interchange (EDI): Standard protocol, available since the 1970s, for electronically transferring information between organizations and across business processes.
- EDI:
- Improves accuracy
- Cuts costs
Integrated Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)
□ Reaping the full benefits of EDI requires that it be fully integrated with the company’s AIS.
E-Business Effects on Value Chain Activities
Information Flows in Electronic Commerce
Financial Electronic Data Interchange (FEDI)
E-Business Success Factors
□ The degree to which e-business activities fit and support the organization’s overall business strategy.
□ The ability to guarantee that e-business processes satisfy the three key characteristics of any business transaction
- Validity
- Integrity
- Privacy
Encryption
There are two principal types of encryption systems:
□ Single-key systems: Same key is used to encrypt and decrypt the message
- Simple, fast, and efficient
- Example: the Data Encryption Standard (DES) algorithm
□ Public Key Infrastructure (PKI): Uses two keys:
- Public key is publicly available and usually used to encode message
- Private key is kept secret and known only by the owner of that pair of keys. Usually used to decode message
Digital Signatures and Digests
□ Digital signature: An electronic message that uniquely identifies the sender of that message.
□ Digest: The message that is used to create a digital signature or digital summary.
- If any individual character in the original document changes, the value of the digest also changes. This ensures that the contents of a business document have not been altered or garbled during transmission
Digital Certificates & Certificate Authorities
□ Digital Certificate: Used to verify the identity of the public key’s owner.
- A digital certificate identifies the owner of a particular private key and the corresponding public key, and the time period during which the certificate is valid.
□ Digital certificates are issued by a reliable third party, called a Certificate Authority, such as:
- Verisign
- Entrust
- Digital Signature Trust
□ The certificate authority’s digital signature is also included on the digital certificate so that the validity of the certificate can also be verified.
Types of Networks
□ The global networks used by many companies to conduct electronic commerce and to manage internal operations consist of two components:
1. Private portion owned or leased by the company
2. The Internet
□ The private portion can be further divided into two subsets:
1. Local area network (LAN) — a system of computers and other devices, such as printers, that are located in close proximity to each other.
2. Wide area network (WAN) — covers a wide geographic area.
□ Companies typically own all the equipment that makes up their local area network (LAN).
□ They usually do not own the long-distance data communications connections of their wide area network (WAN).
□ They either contract to use a value-added network (VAN) or use the Internet.
□ What is an Intranet?
□ The term Intranet refers to internal networks that connect to the main Internet.
□ They can be navigated with the same browser software, but are closed off from the general public.
□ What are Extranets?
□ Extranets link the intranets of two or more companies.
□ Either the Internet or a VAN can be used to connect the companies forming the extranet.
□ Value-added networks (VAN) are more reliable and secure than the Internet, but they are also expensive.
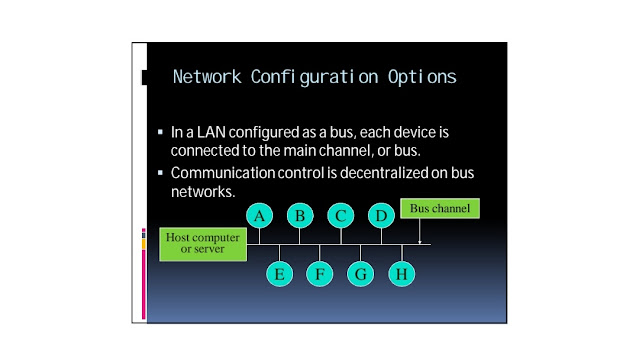
Network Configuration Options
Local area networks (LANs) can be configured in one of three basic ways:
1 Star configuration
2 Ring configuration
3 Bus configuration
A star configuration is a LAN configured as a star; each device is directly connected to the central server.
All communications between devices are controlled by and routed through the central server.
Typically, the server polls each device to see if it wants to send a message.









0 Response to "Introduction: E-Business"
Post a Comment